Custom-built arraylist
In this section, we’ll see how an arraylist holds items and how to implement it.
NOTE: The built-in class for ArrayList in Java holds a collection of objects, not primitive data type, but in our example, we’ll create a collection of double items, for simplicity.
What an ArrayList class looks like
The ArrayList class has an instance variable array that holds the items. If, at the time of triying to add an item, the array is full, then:
- a bigger array is created,
- items from the instance variable array are copied over
- instance variable array is re-referenced to refer to the new, bigger array
Let’s create one such class holding an array of doubles
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public class MyArrayList {
public double[] data;
public int nItems;
public MyArrayList() {
data = new double[5];
nItems = 0; //no item added yet
}
public void add(double itemToAdd) { //THERE IS A PROBLEM HERE
data[nItems] = itemToAdd;
nItems++;
}
}
The client can create an object of class MyArrayList as:
1
2
3
4
5
6
MyArrayList list = new MyArrayList();
list.add(10);
list.add(70);
list.add(20);
list.add(90);
list.add(30);
Five items were added to the list, which is ok. But as soon as you try to add a sixth item using,
1
list.add(80);
The method add will cause,
1
data[5] = 80; //ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
Therefore, we must first check if the internal array is full.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
//inside class MyArrayList
public boolean isFull() {
if(nItems == data.length) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
The method add should be modified as,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
//inside class MyArrayList
public void add(double itemToAdd) {
if(isFull()) {
???
}
data[nItems] = itemToAdd;
nItems++;
}
If the internal array is full,
- a bigger array is created,
- items from the instance variable array are copied over
- instance variable array is re-referenced to refer to the new, bigger array
These steps are performed in a method grow().
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public void grow() {
double[] temp = new double[data.length + 5]; //5 extra items
for(int i=0; i < data.length; i++) { //copy all items over
temp[i] = data[i];
}
data = temp; //make instance variable array refer to the bigger array
}
Updated class definition
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
public class MyArrayList {
public double[] data;
public int nItems;
public MyArrayList() {
data = new double[5];
nItems = 0; //no item added yet
}
public boolean isFull() {
if(nItems == data.length)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public void grow() { //should not be called by outside code
double[] temp = new double[data.length + 5]; //5 extra items
for(int i=0; i < data.length; i++) { //copy all items over
temp[i] = data[i];
}
data = temp; //make instance variable array refer to the bigger array
}
public void add(double itemToAdd) {
if(isFull()) {
grow();
}
data[nItems] = itemToAdd;
nItems++;
}
}
Method to add an item at an arbitrary index
Say, the list contains items [12.5, 6.4, 8.5, 9.6, -3.4] and we want to add an item 16.42 at index 0. All items in the array need to move forward by 1.
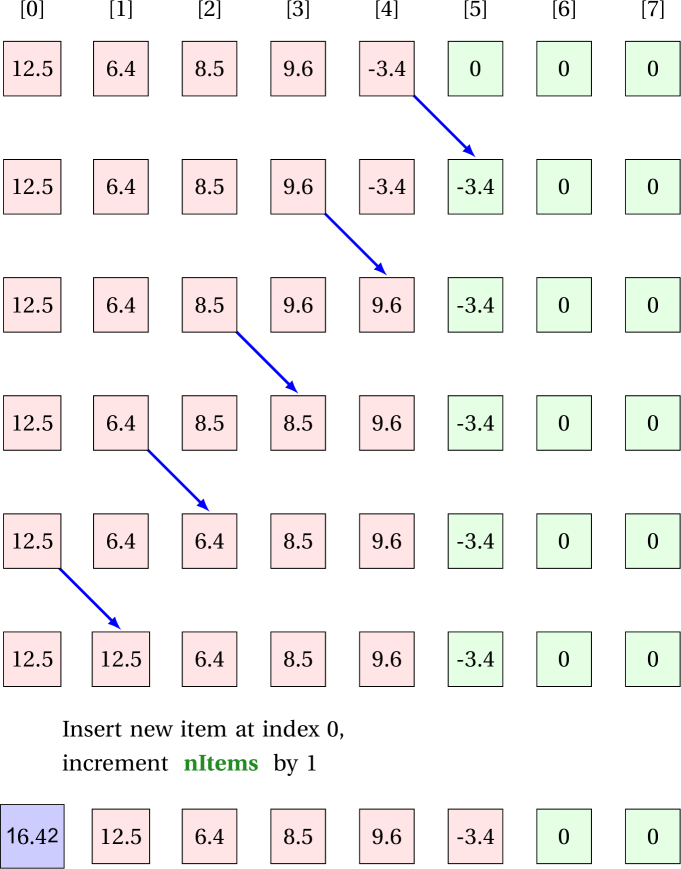
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public boolean add(int idx, double itemToAdd) {
if(idx < 0 || idx > nItems) {
return false; //to indicate failure
}
if(isFull()) {
grow();
}
for(int i=nItems - 1; i >= idx; i--) {
data[i+1] = data[i];
}
data[idx] = itemToAdd;
nItems++;
return true; //to indicate success
}
Method to remove an item from an arbitrary index
Say, the list contains items [12.5, 6.4, 8.5, 9.6, -3.4] and we want to remove the item at index 0. All items in the array need to move backward by 1.
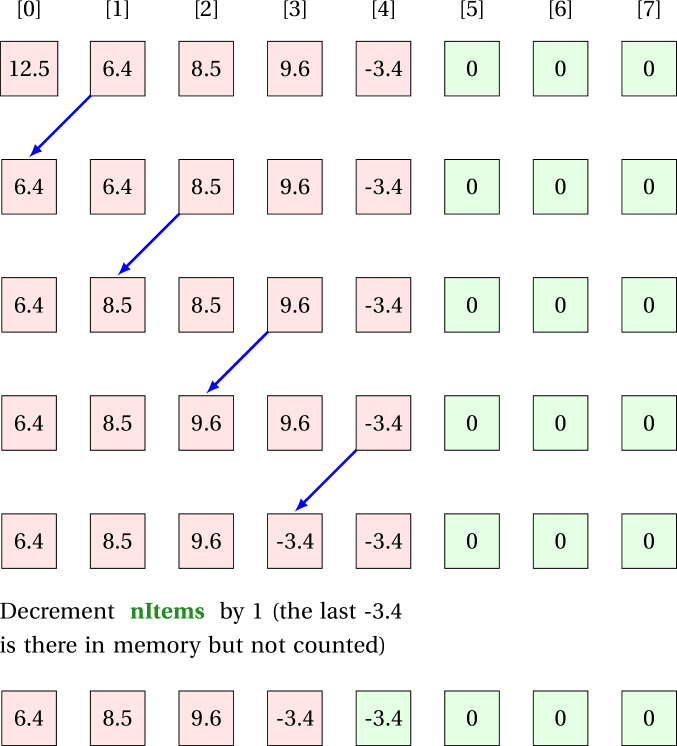
The method should return the item removed.
If we keep the return type as double, what do we return if the index is invalid and therefore no item exists at that index?
Hence, we keep the return type Double since we can return null as error code.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public Double remove(int idx) {
if(idx < 0 || idx >= nItems) {
return null; //error code
}
double itemRemoved = data[idx];
for(int i= idx; i < nItems - 1; i++) {
data[i] = data[i+1];
}
nItems--;
return itemRemoved; //can return double variable as Double
}
NOTE: only when the last item is removed, the above code leaves it in the physical memory (that might be exploited as a vulnerability). You can add the following before decrementing nItems to avoid this:
1
2
3
4
data[nItems-1] = 0;
//reset the last item (since it's been copied to the left anyway
//and then:
//nItems--;
Complete class and client (including homework)
- MyArrayList.java (contains several incomplete methods for practice)
- MyArrayListClient.java
Homework exercises
1. Percentage used
Add an instance method percentageUsed that returns the percentage of the instance array being used. For example, if data.length = 15 and nItems = 12, method returns the value 80.0.
2. indexOf
Add an instance method indexOf that when passed a double, returns the index of the first occurrence of the item. Return -1 if item doesn’t exist. Method header is:
1
public int indexOf(double target)
3. lastIndexOf
Add an instance method lastIndexOf that when passed a double, returns the index of the last occurrence of the item. Return -1 if item doesn’t exist. Method header is:
1
public int lastIndexOf(double target)
4. isValidIndex
Add an instance method isValidIndex that when passed an int (index), returns true if the index is valid, and false otherwise. Method header is:
1
public boolean isValidIndex(int index)
For example, if nItems = 7, indices from 0 to 6 (inclusive on both sides) are valid, and all other indices are invalid.
5. set
Add an instance method set that when passed an int (index) and a double (updated value), sets the item at given index (if within range) to the updated value and returns true. If the index is invalid, return false. Method header is:
1
public boolean set(int index, double updated)
6. Modified growth
Modify the method grow such that the array grows only if full. If the array is not full, it should not grow. Original method (that grows the array irresepective of being full or not) provided below:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public void grow() {
double[] temp = new double[data.length + 5]; //5 extra items
for(int i=0; i < data.length; i++) { //copy all items over
temp[i] = data[i];
}
data = temp; //make instance variable array refer to the bigger array
}
7. Remove an item
Add an instance method remove that when passed a double, removes the first occurrence of the item from the list (if any). The method should return true if there was an instance of the item that was removed, and false if there was no instance of the item in the list. Method header is:
1
public boolean remove(double itemToRemove)
8. Remove all
Add an instance method removeAll that when passed a double, removes all occurrences of the item from the list. You can use the method remove already implemented. The method should return true if there was an instance of the item that was removed, and false if there was no instance of the item in the list. Method header is:
1
public boolean removeAll(double itemToRemove)